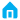
Common malfunctions in automotive air conditioning systems primarily fall into the following categories: cooling problems, abnormal airflow, unpleasant odors, and unusual noises. You can quickly compare symptoms and potential causes below:
I. Common Automotive Air Conditioning Problems
1. Cooling Problems
Typical Symptoms: Insufficiently cool airflow, slow cooling, or complete lack of cooling. These are the most frequently encountered issues, with specific manifestations and causes being relatively diverse.
Main Causes:
- Refrigerant Leakage or Insufficiency: This is the most common cause.
- Poor Condenser Heat Dissipation: Located at the front of the vehicle, the condenser is susceptible to being covered by dust or pollen, which impedes heat dissipation.
- Compressor Malfunction: As a core component, its failure can lead to loss of cooling or unusual noises.
- Excessively Dirty Cabin Air Filter: Severe blockage can affect airflow, indirectly creating a perception of insufficient cooling.
2. Abnormal Airflow
Typical Symptoms: Reduced airflow, no airflow, or malfunctioning airflow direction/temperature control.
Main Causes:
- Clogged Cabin Air Filter: Directly impacts airflow volume.
- Blower Motor Failure: Malfunction of the motor responsible for delivering air.
- Air Duct/Control System Issues: Such as faulty blend door actuators, or problems with control switches or circuits.
3. Odor Problems
Typical Symptoms: Musty or sour smells emitted from the vents when the air conditioning is turned on.
Main Causes:
- Mold Growth on the Evaporator Core and in Air Ducts: After air conditioning operation, condensation easily forms on the evaporator core. This damp environment promotes the growth of bacteria and mold.
- Excessively Dirty Cabin Air Filter: Accumulated dust and microorganisms on the filter can also generate odors.
4. Unusual Noises
Typical Symptoms: Abnormal sounds such as "buzzing" or "clicking" during operation.
Main Causes:
- Foreign Objects or Damage in the Blower Motor: Debris like leaves entering the blower or bearing failure.
- Noisy Compressor: Worn internal components or clutch malfunction.
- Belt or Tensioner Issues: Such as a loose, worn compressor belt or a damaged tensioner pulley.
The above list outlines common potential causes. Actual fault diagnosis should consider the specific vehicle model and circumstances. For malfunctions involving complex components like the compressor or electrical circuits, it is recommended to seek professional repair services.
II. Daily Maintenance and Self-Check Suggestions for Air Conditioning
To enhance the durability and reliability of your air conditioning system, you can follow these maintenance tips:
- Replace the Cabin Air Filter Regularly: This is the most crucial and cost-effective maintenance task. It is generally recommended to replace it every 10,000 to 20,000 kilometers or once a year, ideally around the transition from spring to summer. If you drive in a dusty area, shorten this interval.
- Perform an Air Conditioning System Cleaning at Least Once a Year: Before the summer usage period, a professional cleaning of the air conditioning system is recommended, focusing on the evaporator core and air ducts. This can effectively prevent odors.
- Cultivate Good Daily Usage Habits:
- Turn Off A/C Before Arriving: Turn off the air conditioning cooling function (A/C button) 2-3 minutes before parking, but keep the blower fan running. This allows the moisture on the evaporator core and within the ducts to dry out, reducing mold growth.
- Avoid Prolonged Use of Recirculation Mode: Switch to fresh air mode periodically to maintain air freshness inside the cabin.
- Use High Blower Speed Occasionally: Regularly run the blower at its maximum speed to help reduce dust accumulation within the ducts.
III. Summary of Common Automotive Air Conditioning Issues
In summary, most air conditioning faults are related to refrigerant leaks, dirty or clogged condensers and filters, compressor failure, and internal system moisture. The typical troubleshooting approach is: first, self-check the simplest component—the cabin air filter; then, inspect the external condenser for cleanliness. If the problem persists, professional inspection of the refrigerant and core components is necessary, followed by part replacement if required.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!