Cooling fins are the core components that enhance the effective heat dissipation area of a radiator. The processing methods vary significantly, and the choice depends mainly on material, cost, production volume, fin shape, and performance requirements. The following are several common processing methods for cooling fins currently in use:
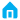
1.Stamping FormingPrinciple: Utilizes the pressure from a die and punch press to plastically deform a metal sheet within the die, thereby obtaining the desired fin shape, as shown in Figure 1. Nowadays, mainstream fin stamping machines or dedicated punch presses are used for high-volume production.
Advantages: Extremely high production efficiency, suitable for large-scale manufacturing; relatively low cost; excellent consistency.
Disadvantages: Requires custom-made dies, resulting in high initial investment; fin height and density are limited; typically produces separate fins that require subsequent bonding to a base plate. Figure 1 Fin Press Forming
Figure 1 Fin Press Forming
2.Roll FormingPrinciple: A long, thin metal strip (usually aluminum) is passed through a precise set of rollers to undergo continuous bending and folding, forming a continuous “zigzag” or corrugated fin strip, as shown in Figure 2.
Advantages: Can produce very high fins with minimal fin spacing, achieving a large heat dissipation area per unit volume; high material utilization rate.
Disadvantages: Relatively low structural strength of fins, prone to deformation; also requires bonding to a base plate.
Main Applications: Automotive radiators (coolers), intercoolers, large industrial heat exchangers. Figure 2 Fin Roll Forming Process
Figure 2 Fin Roll Forming Process
3.Skiving FormingPrinciple: Uses a shaped skiving tool to “scrape” a rotating base plate, plastically deform and stand up a portion of the metal material to form integrated fins with the base plate, as shown in Figures 3 and 4.
Advantages: Fins and base plate are an integrated structure with no contact thermal resistance; capable of producing continuous, high-density fins; flexible design.
Disadvantages: Requires specialized equipment, leading to high initial investment; demands high material ductility (suitable for copper and aluminum).
Main Applications: High-reliability, high-power-density applications, such as military electronic equipment, aerospace, and some high-end plug-in heat sinks.

Figures 3 Skived Aluminum Fins 
Figures 4 Skived Copper Fins
4.Extrusion FormingPrinciple: Heated aluminum or copper billets in a plastic state are forced under high pressure through a die with a specific shaped opening, forming a heat sink profile with integrated fins in a single step.
Advantages: Excellent thermal conductivity (no contact thermal resistance); high structural strength; capable of producing complex solid fin shapes; cost-effective.
Disadvantages: Limited by the extrusion process, the fin aspect ratio (height to spacing) cannot be too high, otherwise it becomes challenging for the die and process; typically produces straight fins.
Main Applications: The most common method for manufacturing heat sinks, widely used in computer CPU coolers, LED lighting heat dissipation, power device cooling, etc.
5.Casting ProcessPrinciple: Molten metal (usually aluminum alloy) is poured into a mold cavity containing the fin shapes. After cooling and solidification, the mold is removed to obtain an integrated heat sink.
Advantages: Extremely high design freedom, capable of producing very complex fin and base structures with curved or irregular shapes; enables integrated design.
Disadvantages: High mold costs; production efficiency is lower than extrusion; internal defects such as pores may exist in castings, affecting thermal conductivity.
Main Applications: Scenarios with special requirements for heat dissipation shape and structure, such as certain high-end graphics card coolers, engine cylinder blocks, and complex thermal management modules.
6.CNC MachiningPrinciple: Uses a CNC milling machine to directly “carve” out fins from a solid metal block by removing material through milling.
Advantages: Highest precision, capable of machining fins of any shape and thinness; no molds required, suitable for prototyping and small-batch production; excellent thermal conductivity (monolithic material).
Disadvantages: Significant material waste, high cost; relatively long machining time.
Main Applications: Aerospace, military, high-end scientific research where performance is critical and cost is not the primary concern; heat sink prototyping.
7.3D Printing / Additive ManufacturingPrinciple: Utilizes metal 3D printing technology (e.g., Selective Laser Melting, SLM) to gradually layer metal powder, directly manufacturing integrated heat sinks with complex internal flow channels and external fins.
Advantages: Maximum design freedom, capable of producing topologically optimized structures and conformal cooling channels that traditional methods cannot achieve, pushing heat dissipation performance to the extreme.
Disadvantages: Extremely high cost; limited printing size; surface roughness may be relatively high.
Main Applications: Cutting-edge technology fields, such as artificial intelligence chip cooling, aerospace vehicles, medical equipment, etc.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!